Electrochemical Cells
An electrochemical cell is a cell that uses redox half reactions to create or use electricity. Voltaic cells are electrochemical cells that create electricity, like a battery. An electrolytic cell is one that uses electricity.
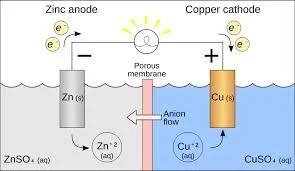
A common one that I will use for this is a zinc and copper cell. The cell is built like this.
On the left is the anode. The anode is the zinc solid which is more active, decreases in size, and goes through oxidation. The zinc half reaction is:
Zn -> Zn⁺² + 2e⁻
The cathode is the right solid which is less active, increases in size, and goes through reduction. It goes through this reaction:
Cu⁺² + 2e⁻ -> Cu
The solution that both the cathode and anode are in is called the electrolytic solution, which holds ions extremely well.
Over time, the zinc anode reacts, causing charged Zn⁺² ions to flow into the solution and the electrons to flow through the wire to the cathode. Meanwhile, the Cu⁺² ions from the solution flow into the cathode, along with the electrons. The flow of electrons through the wire passes what is called the load, which can be anything that serves our purpose with the battery, although in this case, it is a light.
The porous membrane separating the solutions is called a salt bridge. It provides non-reactive ions to move through the solutions and balance out charges. Cations, positively charged ions, flow to the cathode, and anions, negatively charged ions, flow to the anode.
There are three ways that the battery will eventually stop. The first is that the anode mass depletes, and there is nothing to pull the electrons from. The second is that the cathode ion in the solution depletes, and there is no electron flow. Finally, the salt bridge can be depleted, causing there to be no ion charge balance.
In a rechargeable battery, the load is more complicated, having a charger and a discharger. By charging the battery, electrons are simply put into the battery, and they are free to flow in either direction, unlike the above voltaic cell.
The reduction potential lets you know whether the cell is voltaic or electrolytic. Every half reaction has a certain reduction potential which is constant. By adding the reduction potentials of each half reaction, you get your E cell, which, if positive, means a spontaneous reaction, or a voltaic cell/battery. A negative E cell means a nonspontaneous reaction and a nonvoltaic cell, or, in other words, it uses electricity.